JEST facilities are available as a HTTP servlet,
org.apache.openjpa.persistence.jest.JESTServlet.
JESTServlet can be deployed in a servlet container e.g. Tomcat in two
possible modes: primary or auxiliary.
Deployment Modes
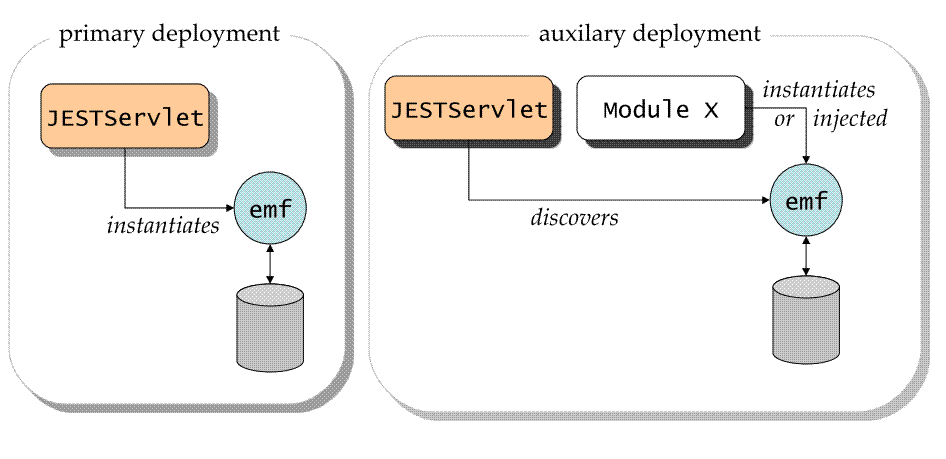
In primary mode, the JESTServlet itself instantiates a persistence
unit during initialization.
In auxiliary mode, the JESTServlet discovers a persistence unit used
by another component X.
The sibling component X must satisfy the following for JEST to discover
its persistent unit
- The component
X and JESTServlet must belong to the same
deployment unit.
- The component
X must activate OpenJPA's native
EntityManagerFactory pool. The pool is activated by switching on
openjpa.EntityManagerFactoryPool configuration property to true.
This property is available only via runtime configuration. The following
code example ensures that OpenJPA's native EntityManagerFactory pool is
active.
Map<String,Object> props = new HashMap<String, Object>();
props.put("openjpa.EntityManagerFactoryPool", "true");
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("myPU",props);
JESTServlet accepts following initial configuration parameters
| Property | Description |
|---|
| persistence.unit | Name of the persistent unit. Must be specified. |
| standalone | true implies primary mode. Defaults to false. |
| debug | true implies verbose tracing of HTTP requests. Defaults to false. |
The following deployment descriptor WEB-INF/web.xml deploys
JESTServlet in auxiliary mode
<web-app version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Demo Application with JEST Servlet</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<description>
An example of deploying a simple web application with JEST servlet.
This descriptor specifies the Demo Application servlet as well as JEST servlet.
</description>
<servlet>
<description>
This is the Demo Application Servlet.
The servlet is mapped to URL pattern /app/* so this servlet can be accessed as
http://host:port/demo/app/
where "demo" is the name of the deployed web application.
Assume that the Demo Application Servlet is using a persistence unit named
'jestdemo'. The JEST Servlet will require the persistence unit name to
browse the Demo Application.
</description>
<servlet-name>demo</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>demo.SimpleApp</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>demo</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- Deployment descriptor for JESTServlet. -->
<servlet>
<description>
This is the JEST servlet.
JEST Servlet needs to know the name of the persistence unit used by the
Demo Application. The unit name is specified by mandatory "persistence.unit"
parameter during initialization.
The JEST servlet is mapped to URL pattern /jest/* in servlet mapping section.
So to access JEST servlet, use the following URI
http://host:port/demo/jest/
Notice the trailing forward slash character is significant.
</description>
<servlet-name>jest</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.openjpa.persistence.jest.JESTServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>persistence.unit</param-name>
<param-value>jestdemo</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>debug</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jest</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/jest/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>